Bleeding gums – tips for healthy gums
What helps when dealing with bleeding gums? When is it time to go to the dentist with your bleeding gums?
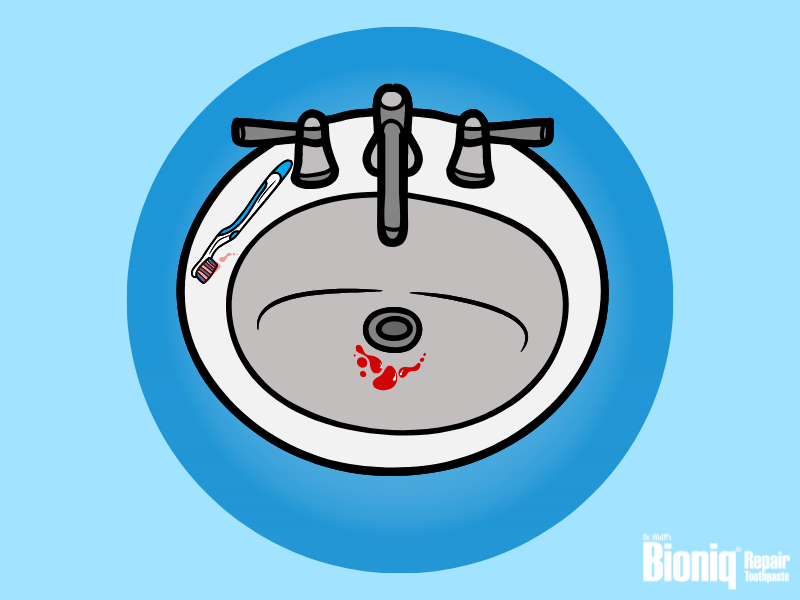
If you discover your gums bleeding, whether between meals, during mealtime or when brushing your teeth, you should make an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible. Healthy gums do not bleed. When gums bleed frequently, are reddened or swollen, this is a first possible sign of gingivitis.
An expert should check to see if there could be serious gum problems at the latest when inflammation is present. Treatment may be required to prevent more serious consequences. Great caution is required, since once gums have receded, they will not grow back.
Apart from treatment by a dentist, or the use of home remedies, there are many other ways to prevent bleeding.
Common causes of bleeding gums
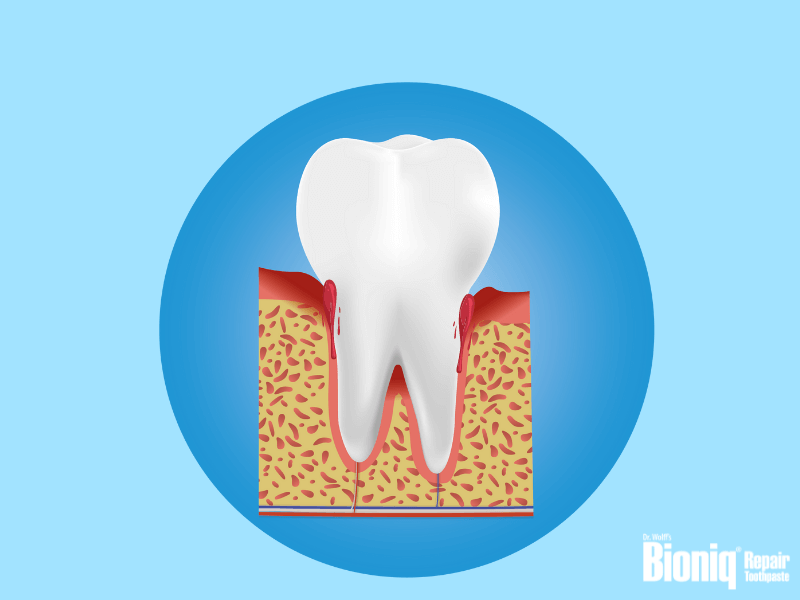
Did you notice blood on your toothbrush or in the sink after brushing your teeth? This is the first sign of a mild form of inflamed gums, also called gingivitis. The cause is almost always bacteria. We have over a billion of them in our mouths and more than 700 species are known to colonize our oral cavity.1 In a healthy state, all these micro organisms balance each other out. Numerous reasons can cause imbalances and just a few bacteria can start gingivitis, which then can result in bleeding gums.
Gingivitis/ inflammation of the gums
Gum inflammation (also called gingivitis) is when the gums are only superficially inflamed. They may also be swollen and reddened. Bacteria settle at the gum line and can penetrate from there into a small natural gap (sulcus) between the tooth and the gum, causing inflammation. These then cause bleeding gums. Even a thorough tooth cleaning can help symptoms subside.
Parodontitis
Parodontitis is a disease of the entire periodontium. In addition to the gums, the so-called ligaments (ligaments that hold the tooth in place) and also the jawbone are affected. There are different stages of parodontitis, which are classified according to their stage. Basically, 4 different stages can be classified depending on the “pocket depth” as well as the overall extent in the oral cavity. In addition, the (possible) progression of the inflammatory periodontal disease is also taken into account during the diagnostic investigation and subsequent diagnosis.2
Nutrient deficiency
Bleeding gums or even gum recession are typical consequences of nutrient or protein deficiency. Vitamin C deficiency can occur in the case of malnutrition, anorexia or excessive alcohol consumption and cause problems in the oral cavity. The same applies to protein deficiency. In particular, tooth loss due to vitamin C deficiency is known in history books as “scurvy”.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, women may experience fluctuations in the body’s hormonal balance. Hormones loosen the tissue in the mouth, making it easier for sensitive areas of the gums to become infected, which can promote inflammation.
Oral hygiene & aggressive brushing techniques
Incorrect or overly aggressive tooth brushing techniques are a common cause of bleeding gums. There are many different scientifically studied tooth brushing techniques. Many of these, for example the so-called BASS technique (small jiggling movements) do not work well in daily life. Therefore, your individual tooth brushing technique should be discussed and practised with the experts from the dental practice.
Diseases
People suffering from diabetes mellitus have an increased risk of gum disease and bleeding gums. Patients with diabetes often have gums that are poorly supplied with blood. In addition, the immune system cannot always react to inflammation in the same way as in healthy individuals. This leads to gum problems in diabetics. It is well studied and shown that parodontitis therapy can improve blood levels, especially in the so-called HbA1 c-value. It is therefore important for individuals with diabetes mellitus to discuss potential treatment options with their doctor and dentist.
Numerous other diseases can lead to an increased tendency of the gums to bleed. These include, for example, leukaemia, HIV and some fungal infections. For this reason, it is important to discuss long-term gum problems with your dentist and doctor.
Medication
Antiepileptic drugs in high doses can cause gum proliferation.
If the immune system is treated with immunosuppressants such as Cyclosporine after organ transplants and autoimmune diseases, bleeding gums can occur as a side effect.
The contraceptive pill or other hormone preparations cause fluctuations – similar to pregnancy – in the hormone balance and promote gum bleeding.
Blood-thinning medication, so-called calcium antagonists, usually increase the risk of plaque and inflammation in the mouth.
When should you visit the dentist with bleeding gums?
If you only rarely suffer from bleeding gums, you do not need to see a dentist immediately. First of all, you should try to clean your teeth better and be gentle on your gums. The right tooth brushing technique and regular professional dental cleaning can help in many cases. However, you are advised to be careful if another disease is already present or you have recently started taking new medication.
You should definitely see the dentist if the bleeding is particularly prolonged, i.e. longer than about 2-3 days, or you feel it is severe, or if your gums have changed visibly over a short period of time. Apart from that, severe gum pain, bad breath, fever or yellow coating on the gums are clear warning signs that you should clarify things with your dentist. Another sign that you should see your dentist is fatigue, which occurs in connection with bleeding gums.
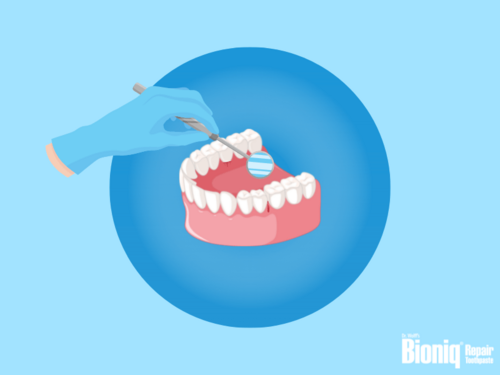
Dental treatment for bleeding gums
- During the initial interview at the dentist’s office, patients are often asked if they have diabetes mellitus, or already know of other diseases they might have such as bleeding disorders, heart disease or osteoporosis. These are the first indicators of the severity of the bleeding gums.
- It is also important for the dentist to know what medication you are currently taking. The question regarding the intensity of the bleeding and the duration of the symptoms are also important for an initial assessment and the right choice of therapy.
- Do you perhaps have an increased and persistent level of stress? Are there also any unhealthy eating habits that could promote bleeding gums? Smokers also carry an increased risk of bleeding gums.
- In the case of female patients, the dentist may inquire about the time of the last menstrual period or ask whether a pregnancy exists.
- After assessing your life circumstances and possible illnesses, the dentist will check your teeth for caries or looseness, because misaligned teeth or areas that are hard to clean, can also lead to increased gum bleeding.
- The overall health of your gums will be checked during this examination. Swelling and redness of the gums can usually be detected visually.
- In addition, a sensor is used to measure whether the gums are already receding and to what extent the gap between the tooth and the gums has deepened.
- When parodontitis is present, additional x-rays are taken to serve as a long-term check for monitoring potential bone loss.
What helps when dealing with bleeding gums?
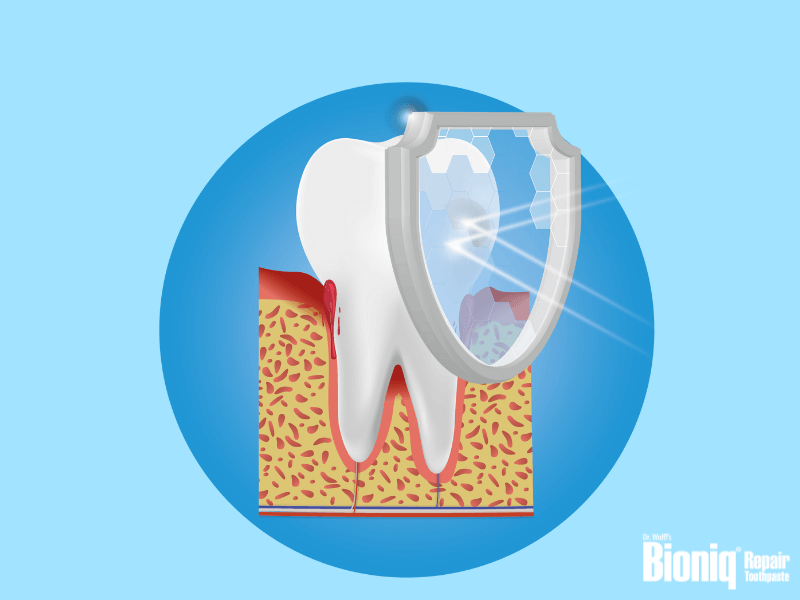
There are different ways to protect yourself from bleeding gums. These usually have a preventative effect:
- Brushing your teeth regularly: It is advisable to brush your teeth twice a day to prevent plaque bacteria from settling on the gum line and promoting inflammation. Appropriate toothpastes for bleeding gums also help, such as Bioniq Repair-Toothpaste Plus, with the active ingredient lactoferrin and hyaluron, which support the care of your gums and protect them from inflammation.
- Using a mouth rinse: Using a mouth rinse after brushing your teeth also helps prevent bleeding gums.
- Cleaning the interdental spaces: You can clean the interdental spaces with dental floss or interdental brushes, as a supplement to your daily oral care routine. The following applies here: Consult your dentist for tips on proper usage.
- Have your teeth professionally cleaned: At least twice a year, plaque and fixed tartar should be removed by professional dental cleaning as a part of the prophylaxis examinations at the dentist. Removing plaque means there is less surface for bacteria to attack. This can prevent inflammation and bleeding gums.
- Clean your tongue: Using a tongue scraper, you can remove germs that sit on your tongue, which also reduces the risk of gingivitis.
- Eat less sugar: Excessive consumption of sugar promotes the growth of bacteria in your mouth. In particular, small, sugary snacks spread throughout the day stimulate the growth of caries bacteria. To provide less target surface during the day, either brush your teeth in between meals or at least use sugar-free chewing gum for oral care.
- A healthy, balanced diet: Less sugar and alcohol and an adequate intake of protein and vitamin C are important factors in preventing bleeding gums.
Home remedies for bleeding gums
Simple remedies using things you have at home, can have a supportive effect in your fight against bleeding gums. Sage and chamomile teas, among others, are considered particularly reliable in inhibiting inflammation.
This may also be of interest to you

Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis)
If your gums are reddened, swollen or even bleeding, these may be signs of gingivitis. In this article you will learn how to detect inflamed gums, how good oral hygiene promotes healing and when gingivitis means a visit to the dentist.

Periodontitis
Periodontitis – also known as gum disease – is inflammation of the tooth socket. In many patients, this disease goes unnoticed for some time, as there are only a few symptoms during the initial stages. In this article you will find out how to recognise periodontitis and how to treat it.

Enamel
Tooth enamel is the hardest substance in the human body. Over time, however, it is worn away. In this article you will learn what enamel is, what function it has for oral health, how to detect enamel wear and how to restore your own enamel.
Sources:
- Meyer, F. & Enax, J. Die Mundhöhle als Ökosystem. Biol. Unserer Zeit 48, 62-68 (2018).
- Jepsen, S.: Neue PAR-Klassifikation, neue PAR-Leitlinie, neue PAR-Richtlinie. Kassenzahnärztliche Vereinigung, 05-2021.